Both gas shocks and oil shocks have their advantages and suitable applications. In this article, we'll delve into the key factors that distinguish gas shocks from oil shocks, understand their differences, helping you make an informed decision that aligns with your specific needs.
Definitions and Performance
Gas Shocks
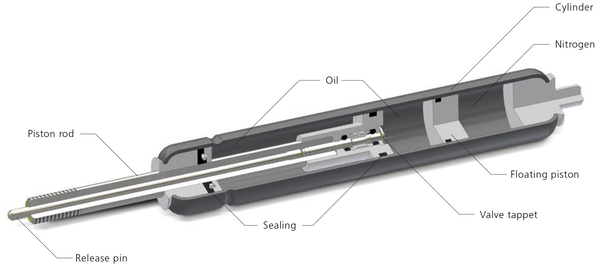
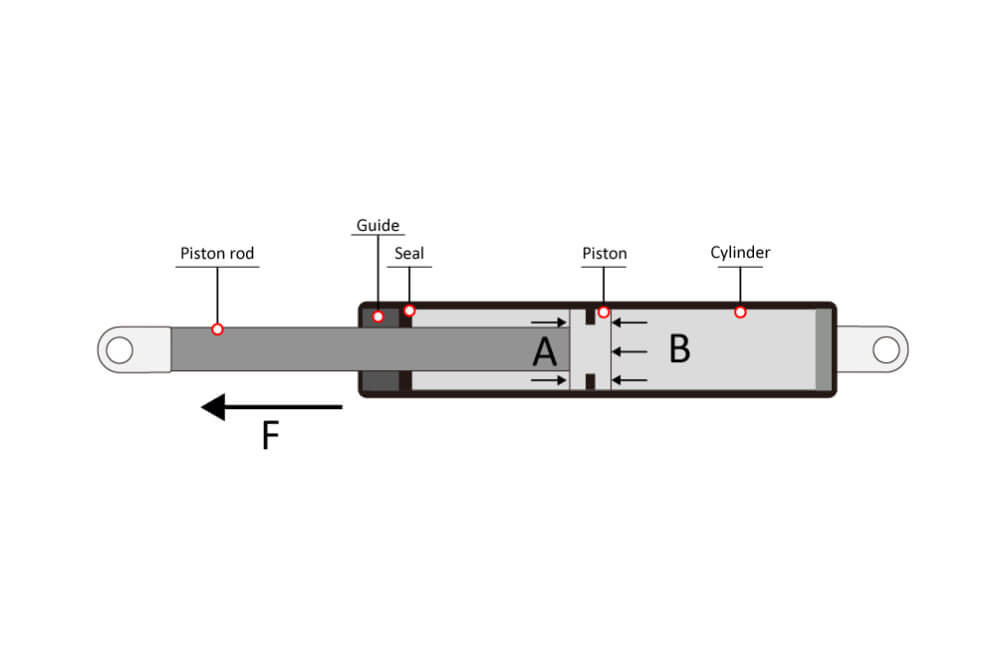
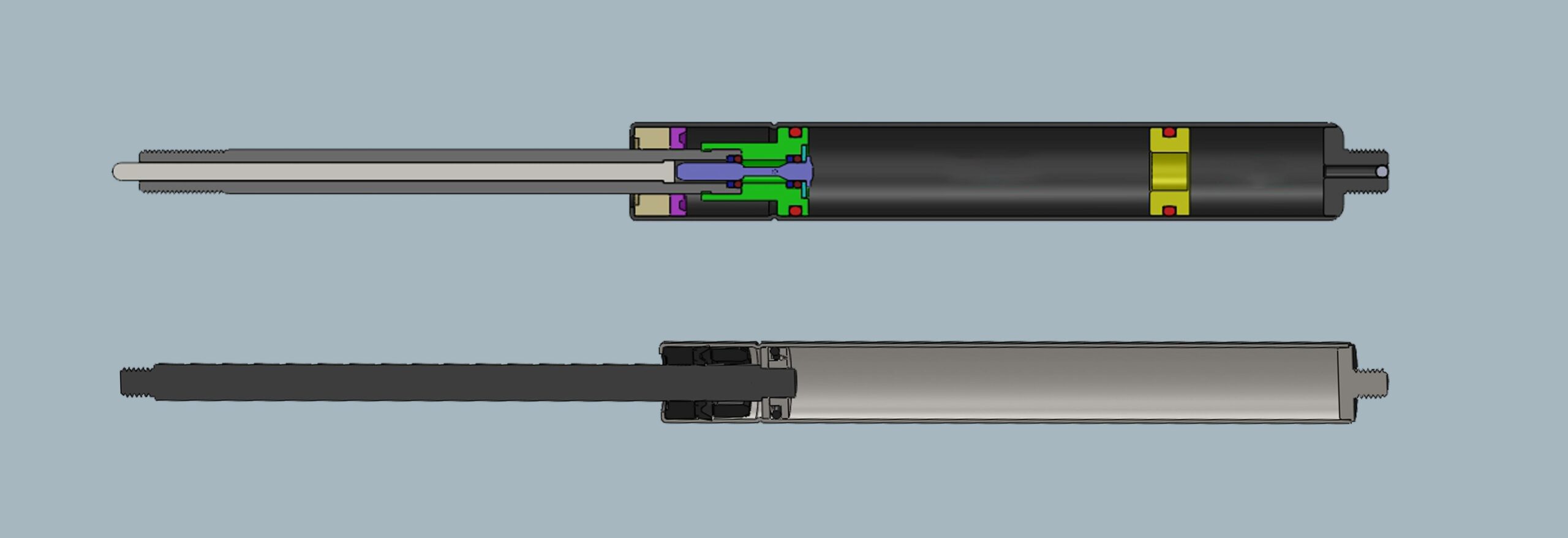
Gas shocks, also known as gas-charged shocks or gas springs or gas struts, contain certain amount of pressurized nitrogen gas along with small amount of hydraulic oil. This gas can providing more consistent and responsive damping performance. It prevents shock fade during continuous use, making gas shocks ideal for heavy-duty and high-performance applications.
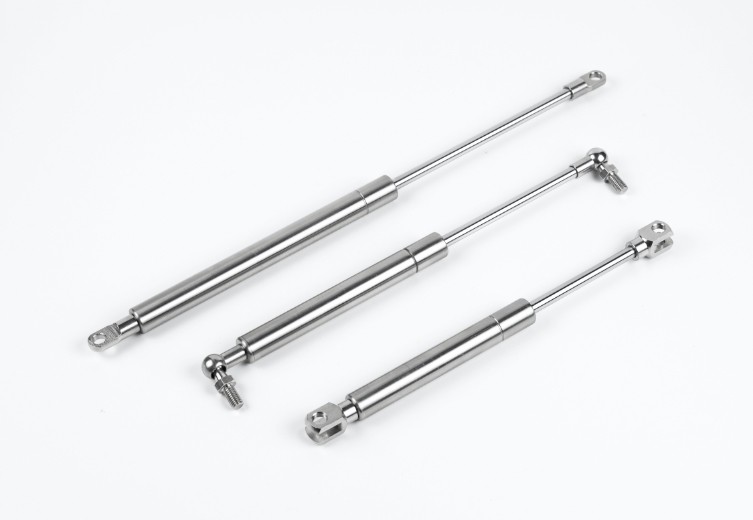

Oil Shocks
Oil shocks, on the other hand, use hydraulic fluid (oil) to absorb and dissipate the energy from road. While they offer reliable performance for everyday driving and general use, they may experience a bit more shock fade under extreme conditions compared to gas shocks.
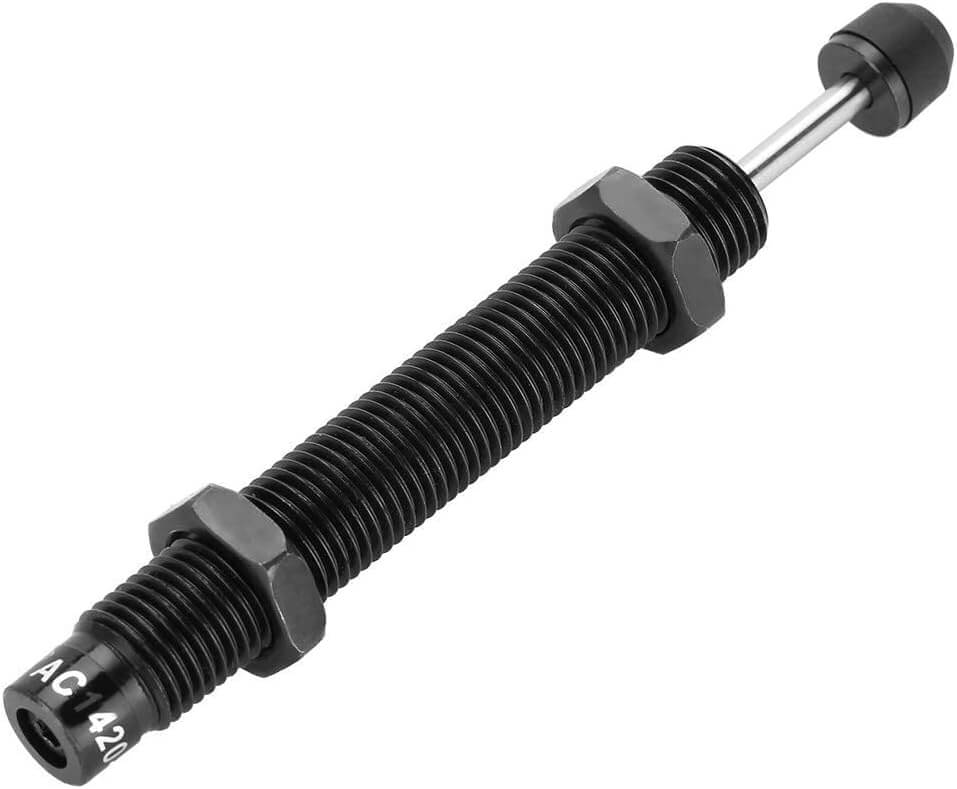
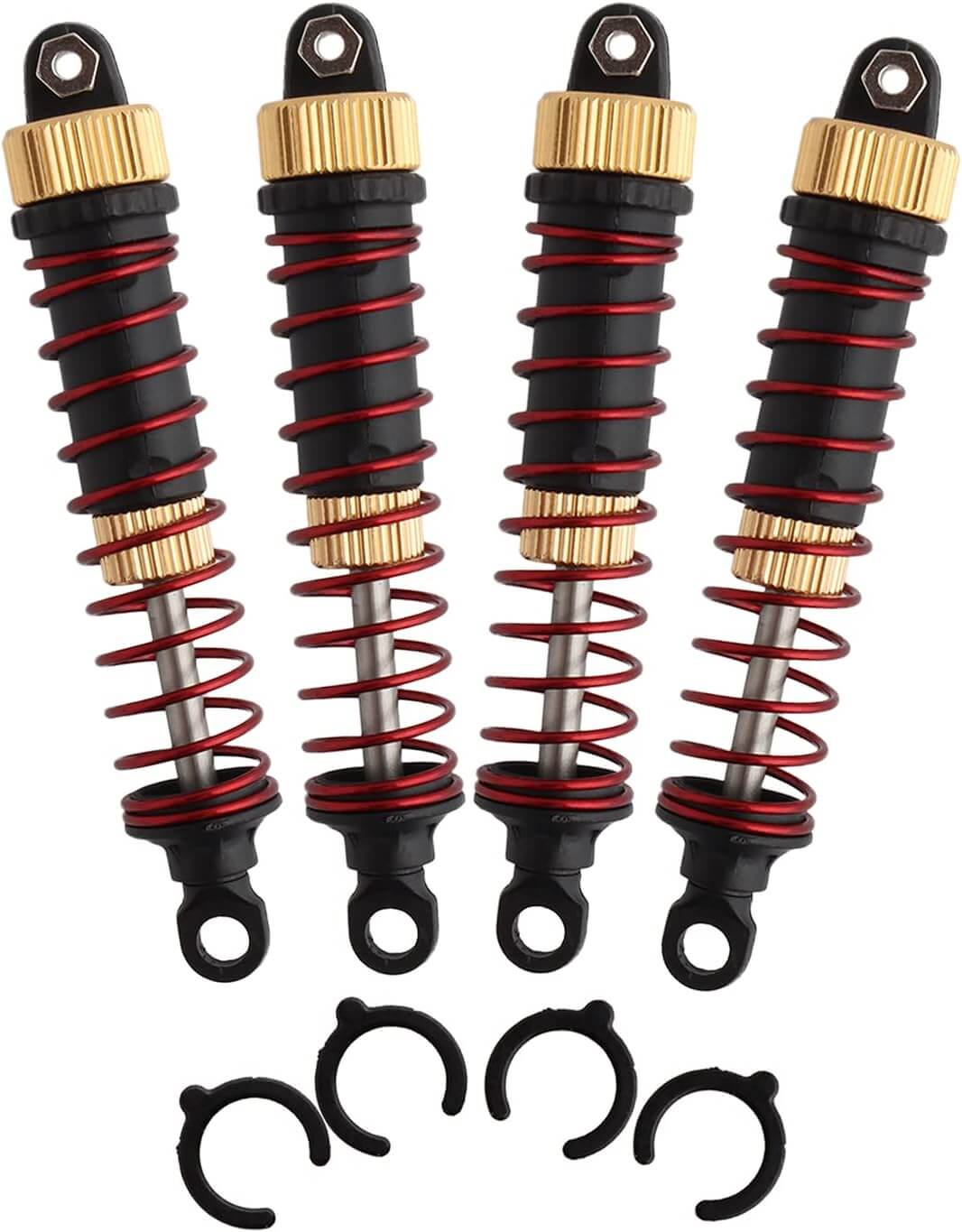


Heat Dissipation and Cooling Difference
Gas Shocks
The presence of nitrogen gas in gas shocks aids in dissipating heat, which is generated during prolonged and aggressive use. This heat dissipation capability allows gas shocks to maintain consistent damping performance, even during demanding conditions.
Oil Shocks
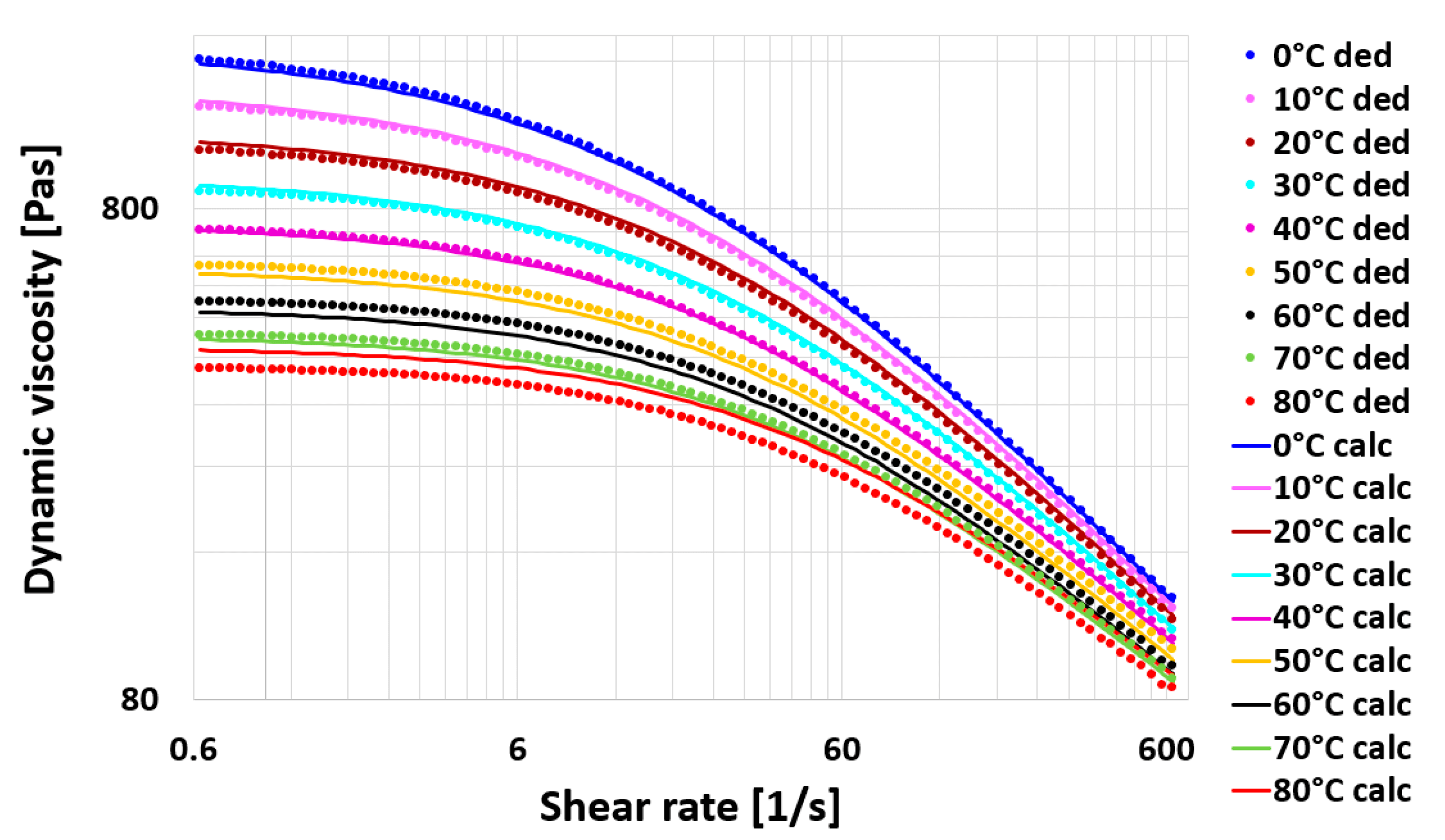
While oil shocks may not dissipate heat as efficiently as gas shocks, they still offer dependable performance for regular driving and moderate usage. However, extended heavy use may lead to increased heat buildup, resulting in temporary loss of damping effectiveness. Below is the the effect of temperature on silicon oil viscosity.
Load Capacity Difference
Gas Shocks
Gas shocks generally have a higher load-carrying capacity due to the pressurized nitrogen gas assisting the hydraulic fluid in supporting heavy loads. This makes them suitable for trucks, SUVs, and other vehicles involved in hauling or towing tasks.

Oil Shocks
While oil shocks are reliable for standard loads, they might not handle heavy loads as effectively as gas shocks. For vehicles that carry significant weight regularly, gas shocks may be the preferred choice.
Price and Maintenance
Gas Shocks
Gas shocks are often priced slightly higher than oil shocks due to their advanced design and performance capabilities. However, the initial investment can be justified by their extended lifespan and superior performance under demanding conditions.
Oil Shocks
Oil shocks are generally more budget-friendly, making them an attractive option for those seeking cost-effective solutions. They require standard maintenance, such as regular inspections and fluid replacements, to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both gas shocks and oil shocks have their distinct advantages and are suited for different applications. Gas shocks excel in high-performance and heavy-duty scenarios, offering superior damping performance and heat dissipation. On the other hand, oil shocks provide reliable and economical performance for everyday driving and moderate use. Understanding your specific needs and the demands of your application will help you make an informed decision and choose the ideal shock absorbers for your vehicle or equipment.