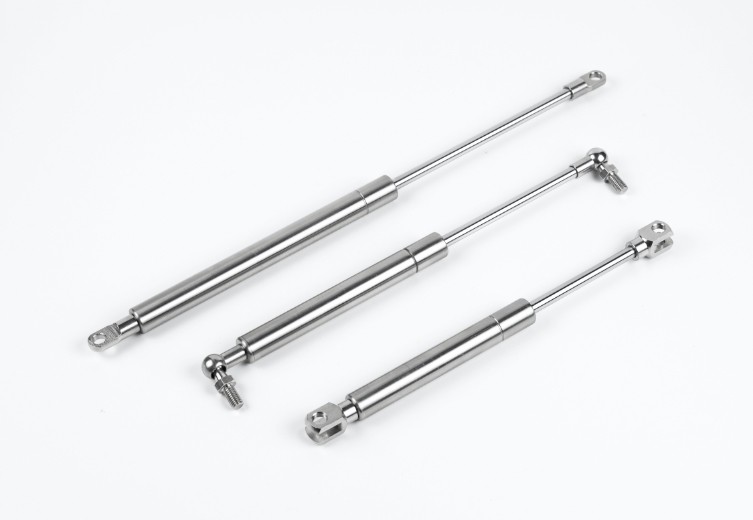
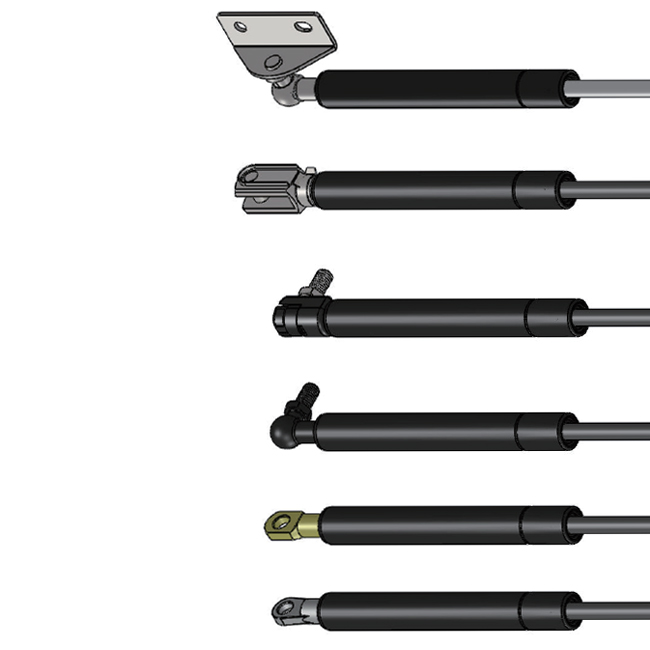
A gas spring is mechanical device that uses compressed gas, typically nitrogen, to provide a pushing force. It works on the principle of Pascal’s Law.
Gas springs are piston-cylinder devices that use pressurized nitrogen as medium to produce a force. But how is the force generated, and how big is it?
As you can see from the sectional view of a gas spring below, Area A is always a bit smaller than Area B, which is caused by the rod area. The surface area difference on both sides of the piston generates the force. So, theoretically the force of a gas spring can be calculated by this simple formula:
F=P*(B-A)
P means the gas pressure inside.
B minus A means the area difference.
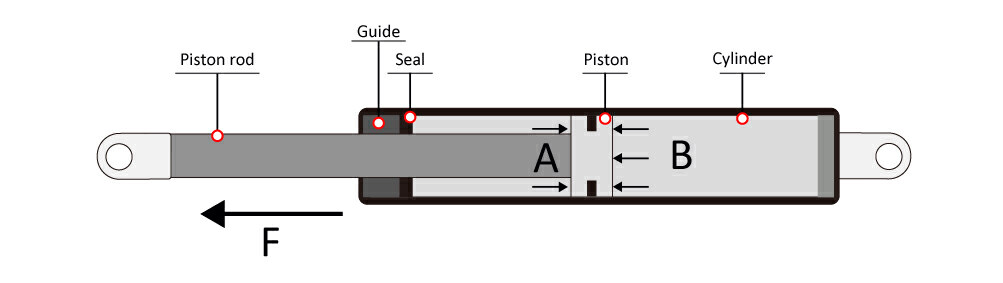
When gas spring compresses or extends, gas can move through a hole(or a valve) from one side to another, maintaining pressure on both sides. Also, the net compression or extension force will near-constant.
Gas springs are generally considered to have near-constant force throughout the stroke, with a k-factor indicating the slight increase.
This Video Explains How Gas Spring Works: